Table of Contents
What is Baricitinib?
Baricitinib is an excellent drug used to prepare medicine that treats rheumatoid arthritis in adults. Baricitinib is useful for patients who have not responded actively or are tolerant to other primary disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. This API can be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate.
Baricitinib is also sold under the trade name Olumiant. It is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor [JAK1 and JAK2]. Overactive JAK inhibitors are known for autoimmune disorders such as alopecia and rheumatoid arthritis. Hence, Baricitinib inhibits the actions of JAK1 and JAK2 to mitigate those autoimmune diseases.
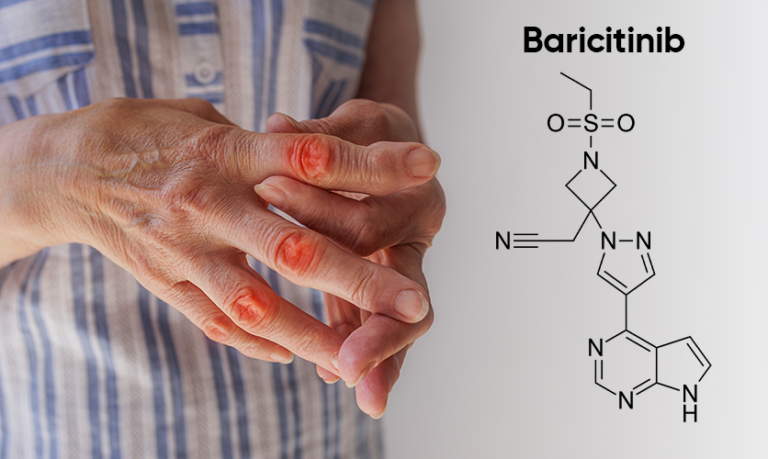
Here’s the chemical structure of Baricitinib API:
The other chemical details of Baricitinib API are as follows:
Chemical Formula: C16H17N7O2S
Molar Mass: 371.4
CAS Number: 1187594-09-7
InChI Key: XUZMWHLSFXCVMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPAC Name: 2-[1-ethylsulfonyl-3-[4-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)pyrazol-1-yl]azetidin-3-yl]acetonitrile
SMILES: CCS(=O)(=O)N1CC(CC#N)(C1)N2C=C(C=N2)C3=C4C=CNC4=NC=N3
What are the Most Common Uses of Baricitinib?
Here are the most common uses of Baricitinib API:
- Baricitinib API is an inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2, having anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, and antineoplastic properties.
- The medicine is widely used to treat rheumatoid arthritis in adults.
- Baricitinib API can also be used to treat other autoimmune diseases in adults.
- Baricitinib is specifically given to patients having moderate or severe arthritis that have shown no improvements or could not tolerate any of the tumor necrosis factor antagonists.
Organizations and Clinical Trials of Baricitinib
Fifty-four organizations clinically tested Baricitib API for research and development purposes. However, one organization also tested it for marketing purposes. The trials for Baricitinib API were conducted in four phases, and a total of ninety-one trials were held successfully.
A few organizations that participated in the testing of Baricitinib API were:
- Eli Lilly
- Incyte
- Genuine Research Centre, Egypt
- Galvani Bioelectronics
Indications of Baricitinib API
There is one approved indication of Baricitinib API:
- Arthritis, Rheumatoid
There are forty experimental indications of the Baricitinib API as concluded in the four trials:
- Alopecia Areata (Phase 3)
- Arthritis, Juvenile (Phase 3)
- Arthritis, Rheumatoid (Phase 4)
- Bone Density (Phase 3)
- Communicable Diseases, Emerging (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Coronavirus Infections (Phase 3)
- COVID-19 (Phase 4)
- Dermatitis, Allergic Contact (Early Phase 1)
- Dermatitis, Atopic (Phase 3)
- Dermatomyositis (Phase 3)
- Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 (Phase 2)
- Diabetic Nephropathies (Phase 2)
- Finger Joint (Phase 3)
- Giant Cell Arteritis (Phase 2)
- Gout (Phase 3)
- Graft vs. Host Disease (Phase 2)
- Healthy Volunteers (Phase 1)
- Hepatic Insufficiency (Phase 1)
- Hereditary Autoinflammatory Diseases (Phase 3)
- Inflammation (Phase 1)
- Lipodystrophy (Phase 3)
- Livedoid Vasculopathy (Phase 3)
- Liver Cirrhosis, Biliary (Phase 2)
- Liver Diseases (Phase 1)
- Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic (Phase 3)
- Myalgia (Phase 2)
- Myositis (Phase 2)
- Pharmacology (Phase 3)
- Pneumonia (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Pneumonia, Viral (Phase 3)
- Psoriasis (Phase 2)
- Pyoderma (Phase 2)
- Pyoderma Gangrenosum (Phase 2)
- Sjogren’s Syndrome (Phase 2)
- Skin Diseases (Phase 2)
- Skin Diseases, Papulosquamous (Phase 2)
- Skin Ulcer (Phase 2)
- Uveitis (Phase 3)
- Vitiligo (Phase 2)
- Wound Healing (Phase 2)
Read Also: Everything You Need to Know about Apremilast
Safety and Hazards for Baricitinib API
Pictogram(s): Irritant, Health Hazard, Environmental Hazard
Signal: Danger
GHS Hazard Statements: H302 (50%), H360 (75%), H373 (75%), H411 (75%)
Precautionary Statement Codes: P203, P260, P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+P317, P318, P319, P330, P391, P405, and P501
Pharmacology of Baricitinib
Mechanism of Action: Tyrosine-protein kinase JKA1 inhibitor, Tyrosine-protein kinase JKA2 inhibitor
Black Box: No
Pro Drug: No
ALogP: 1.1
Associated Conditions: Alopecia Areata (AA), Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‑19), Severe Atopic Dermatitis, Moderate Atopic dermatitis, Moderate, active Rheumatoid arthritis, Severe, active Rheumatoid arthritis
Protein Building: 50% bound to plasma proteins and 45% bound to serum proteins
Half-life: 12 hours
Technology: Synthetic
Common Side Effects of Baricitinib
Although Baricitinib is quite useful in treating rheumatoid arthritis in adults, there are some common side effects associated with this medication. To name a few, we have:
- nausea
- headache
- acne
- red bumps or pimples around hair follicles
Patients experiencing facial swelling or stomach pain should immediately consult their doctors.
Who Should Not Take Baricitinib?
Baricitinib is a good medicine for treating arthritis in adults. However, you must limit yourself from this drug under these situations:
- You must not take this medicine if allergic to Baricitinib API or any other drug used to prepare this medicine.
- You should also consult your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Patients with anemia, ulcers, and liver disease must also limit themselves from taking this medicine.
How to Store and Dispose of Baricitinib?
You must store Baricitinib API in an air-tight and tightly-closed container away from the reach of children. The medicine must be stored in a place having limited moisture and heat. Baricitinib API is not child-resistant and may be poisonous for your children.
Due to such hazardous nature, Baricitinib API must never be disposed of in the open. You should never flush or throw away unused Baricitinib medicines. Instead, one must follow the FDA’s medicine take-back program to dispose of Baricitinib API. You can check the FDA’s Safe Disposal of Medicines website to learn more about it.
Conclusion
Baricitinib is an inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2, tyrosine protein kinases. The medicine limits the overactivity of JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitors, relieving patients from rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. Baricitinib API is sold under the brand name Olumiant and has a molar mass of 371.4.
Patients with an allergy to Baricitinib or other related drugs must limit themselves from this medicine. Some common side effects of Baricitinib include headache, acne, and red bumps. Forty-four organizations tested Baricitnib API in four phases. A total of ninety-one trials were conducted successfully.