Ibrutinib belongs to a class of kinase inhibitors that treats chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). It is sold under the brand name Imbruvica. Ibrutinib irreversibly binds the BTK protein, thereby inhibiting the B-cell receptor pathway, which is active in B-cell cancers. Besides CLL, Ibrutinib is also used to treat mantle cell lymphoma and Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia.
Enquire Now
What is Ibrutinib?
Product Description
Molar Mass: 440.4971
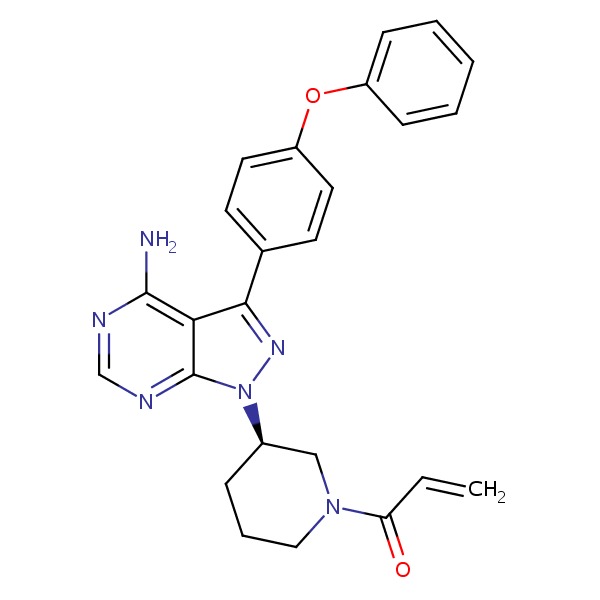
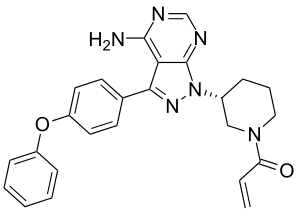
SMILES: NC1=C2C(=NC=N1)N(N=C2C3=CC=C(OC4=CC=CC=C4)C=C3)[C@@H]5CCCN(C5)C(=O)C=C
InChIKey: XYFPWWZEPKGCCK-GOSISDBHSA-N
ALogP: 4.22
CAS Number: 936563-96-1
Chemical Formula: C25H24N6O2
Form: Oral
Protein Binding: 97.3%
Solubility: DMF: 30 mg/ml, DMSO: 30 mg/ml, DMSO:PBS(pH 7.2) (1:3): .25 mg/ml, Ethanol: .25 mg/ml
Storage: -20°C
Suitable for: Adults
IUPAC Name:
1-[(3R)-3-[4-amino-3-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]-1-piperidinyl]-2-propen-1-one
Approved Indications: 3
As per the clinical trials, there are three major approved indications of the Ibrutinib drug:
- Leukemia, Lymphocytic, Chronic, B-Cell
- Lymphoma, Mantle-Cell
- Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia
Experimental Indications: 94
As per clinical trials 1-4, the drug can be used in the following categories:
- Agammaglobulinaemia Tyrosine Kinase (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Amyloidosis (Phase 2)
- Anemia (Phase 3)
- Anemia, Aplastic (Phase 2)
- Anemia, Hemolytic, Autoimmune (Phase 2)
- Anemia, Refractory (Phase 2)
- Antigens, CD20 (Phase 2)
- Body Weight (Phase 2)
- Bone Marrow Failure Disorders (Phase 2)
- Breast Neoplasms (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Burkitt Lymphoma (Phase 2)
- Carcinoid Tumor (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Renal Cell (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Transitional Cell (Phase 2)
- Central Nervous System Neoplasms (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Chromosome Aberrations (Phase 2)
- Colonic Diseases (Phase 2)
- Colonic Neoplasms (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Colorectal Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- COVID-19 (Phase 2)
- Cyclin D1 (Phase 2)
- Cyclin D2 (Phase 2)
- Cyclin D3 (Phase 2)
- Drugs, Investigational (Phase 2)
- Ependymoma (Phase 1)
- Esophageal Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Fever (Phase 2)
- Food (Phase 2)
- Food Hypersensitivity (Phase 2)
- Glioblastoma (Phase 1)
- Graft vs. Host Disease (Phase 4)
- Head and Neck Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Healthy Volunteers (Phase 1)
- Hematologic Neoplasms (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (Phase 2)
- Hepatitis B, Chronic (Phase 3)
- HIV Infections (Phase 1)
- Hodgkin Disease (Phase 2)
- Hyperplasia (Phase 1)
- Immunoglobulin Light Chains (Phase 2)
- Infections (Phase 2)
- Intestinal Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Intraocular Lymphoma (Phase 2)
- Leukemia (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, B-Cell (Phase 4)
- Leukemia, Biphenotypic, Acute (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Hairy Cell (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Lymphocytic, Chronic, B-Cell ()
- Leukemia, Lymphoid (Phase 3)
- Leukemia-Lymphoma, Adult T-Cell (Phase 1)
- Leukemia, Mast-Cell (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Myelogenous, Chronic, BCR-ABL Positive (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Leukemia, Myelomonocytic, Chronic (Phase 1)
- Leukemia, Prolymphocytic (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Prolymphocytic, B-Cell (Phase 1)
- Leukemia, Prolymphocytic, T-cell (Phase 2)
- Liver Diseases (Phase 1)
- Lung Neoplasms (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Lymphoma (Phase 3)
- Lymphoma, AIDS-Related (Phase 1)
- Lymphoma, B-Cell (Phase 4)
- Lymphoma, B-Cell, Marginal Zone (Phase 3)
- Lymphoma, Follicular (Phase 3)
- Lymphoma, Large B-Cell, Diffuse (Phase 3)
- Lymphoma, Large-Cell, Immunoblastic (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, Mantle-Cell ()
- Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin (Phase 4)
- Lymphoma, Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, T-Cell (Phase 1)
- Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis (Phase 1)
- Mastocytosis, Systemic (Phase 2)
- Medulloblastoma (Phase 1)
- Melanoma (Phase 2)
- Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (Phase 2)
- Multiple Myeloma (Phase 2)
- Mutation (Phase 3)
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes (Phase 2)
- Neoplasm Metastasis (Phase 2)
- Neoplasms ()
- Neuroectodermal Tumors (Phase 1)
- Pancreatic Neoplasms (Phase 3)
- Precursor B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma (Phase 2)
- Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma (Phase 2)
- Prostatic Neoplasms (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Recurrence (Phase 2)
- Risk Factors (Phase 2)
- Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (Phase 2)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck (Phase 2)
- Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (Phase 2)
- Stomach Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Testicular Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia ()
Clinical Trials:
A total of 313 trials took place in four phases for Ibrutinib. One hundred fifty (150) organizations participated in those trials.
Side Effects:
Major side effects observed after the consumption of Ibrutinib are:
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
Product CAS No
936563-96-1
Therapeutic Action
Ibrutinib is used to treat certain cancers (such as mantle cell or marginal zone lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia). Ibrutinib belongs to a class of drugs known as kinase inhibitors. It works by slowing or stopping the growth of cancer cells.
Conclusion
Ibrutinib is a drug that adults use to treat cancer symptoms. It is used to treat CLL, MCL, and Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia. The molar mass of Ibrutinib is 440.49 g/mol and is represented by the chemical formula C25H24N6O2. There are many other experimental indications of Ibrutinib, such as Hepatitis B, COVID 19, Hyperplasia, etc. Some common side effects of this drug are headache, vomiting, and diarrhea.