Niraparib is an anti-cancer drug sold under the brand name Zejula. It is used in tablet form to treat epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer. The drug belongs to a class of medication called poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors. Niraparib showed excellent results in treating the above types of cancer. Moreover, it is also being tested to treat ovarian and breast cancer in adults.
Enquire Now
What is Niraparib?
Product Description
Molar Mass: 320.40
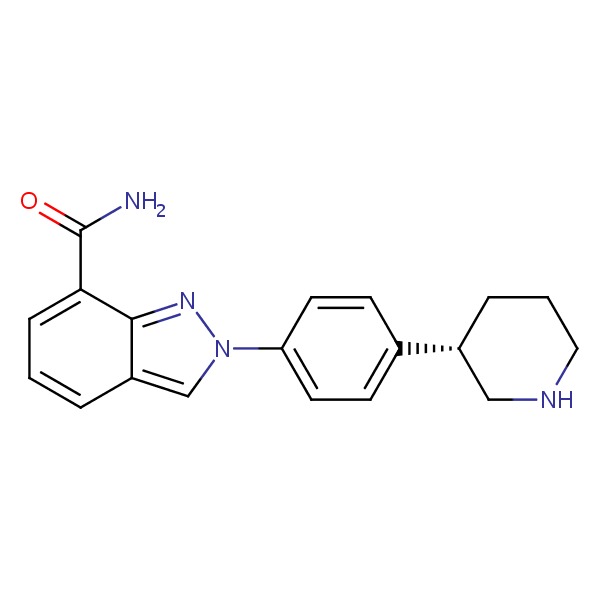
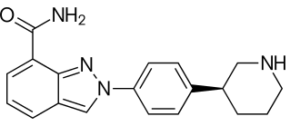
SMILES: c1cc2cn(nc2c(c1)C(=O)N)c3ccc(cc3)[C@@H]4CCCNC4
InChIKey: PCHKPVIQAHNQLW-CQSZACIVSA-N
ALogP: 2.59
CAS Number: 1038915-73-9
Chemical Formula: C19H20N4O
Form: Tablets
Protein Binding: 83%
Bioavailability: 73%
Solubility: DMF: 30 mg/ml, DMSO: 30 mg/ml, DMSO:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:6): 0.14 mg/ml, Ethanol: 1 mg/ml
Storage: -20°C
Suitable for: Adults
IUPAC Name: 2-[4-[(3S)-3-Piperidyl]phenyl]indazole-7-carboxamide
Approved Indications: 3
As per the clinical trials, there are three major approved indications of the Niraparib drug:
- Fallopian Tube Neoplasms
- Ovarian Neoplasms
- Peritoneal Neoplasms
Experimental Indications: 65
As per clinical trials 1-4, the drug can be used in the following categories:
- Adenocarcinoma (Phase 2)
- Adnexal Diseases (Phase 2)
- Angiogenesis Modulating Agents (Phase 2)
- Antineoplastic Agents (Phase 2)
- Bevacizumab (Phase 2)
- Biliary Tract Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- BRCA1 Protein (Phase 3)
- Breast Neoplasms (Phase 3)
- Carcinoma (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Neuroendocrine (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung (Phase 3)
- Carcinoma, Ovarian Epithelial (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Renal Cell (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Transitional Cell (Phase 2)
- Cholangiocarcinoma (Phase 2)
- Colorectal Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Endocrine Gland Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Endocrine System Diseases (Phase 2)
- Endometrial Neoplasms (Phase 3)
- Enzyme Inhibitors (Phase 2)
- Esophageal Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Fallopian Tube Neoplasms (Phase 3)
- Genital Diseases, Female (Phase 2)
- Genital Neoplasms, Female (Phase 2)
- Glioblastoma (Phase 2)
- Glioma (Early Phase 1)
- Gonadal Disorders (Phase 2)
- Hamartoma (Phase 3)
- Head and Neck Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Homologous Recombination (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Lymphocytic, Chronic, B-Cell (Phase 1)
- Leukemia, Prolymphocytic, T-cell (Phase 1)
- Liver Diseases (Phase 1)
- Lung Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, Mantle-Cell (Phase 2)
- Melanoma (Phase 2)
- Mesothelioma (Phase 2)
- Microsatellite Instability (Phase 2)
- Molecular Mechanisms of Pharmacological Action (Phase 2)
- Mutation (Phase 3)
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (Phase 2)
- Neoplasm Metastasis (Phase 2)
- Neoplasms ()
- Neoplasms by Histologic Type (Phase 2)
- Neoplasms by Site (Phase 2)
- Neoplasms, Glandular, and Epithelial (Phase 2)
- Ovarian Diseases (Phase 3)
- Ovarian Neoplasms (Phase 4)
- Pancreatic Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Peritoneal Neoplasms (Phase 3)
- Prostatic Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Prostatic Neoplasms, Castration-Resistant (Phase 3)
- ras Proteins (Phase 2)
- Rectal Neoplasms (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Sarcoma, Ewing (Phase 1)
- Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (Phase 3)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck (Phase 2)
- Stomach Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Treatment Outcome (Phase 2)
- Triple-Negative Breast Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Urinary Bladder Neoplasms (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Urogenital Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Uterine Cervical Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Uterine Neoplasms (Phase 2)
Clinical Trials:
A total of 131 trials were held for Niraparib in four phases. One hundred and thirty (130) organizations participated in these trials.
Side Effects:
Major side effects observed after the consumption of Niraparib are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Product CAS No
1038915-60-4
Therapeutic Action
Niraparib is used to help maintain the response of certain types of ovarian (female reproductive organs where eggs are formed), fallopian tube (tube that transports eggs released by the ovaries to the uterus), and peritoneal (layer of tissue that lines the stomach). It is also used to treat certain types of ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer. It is called poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors.
Conclusion
Niraparib is an anti-cancer drug used to treat fallopian tubes, epithelial ovarian, and primary peritoneal cancer. It is generally stored at room temperature and has more than two years of stability. The molar mass of Niraparib is 320.396 g/mol, and the formula C19H20N4O represents it. Besides cancer, it has several other experimental indications, including Rectal Neoplasm, Uterine Neoplasm, Carcinoma, etc. Some common side effects of Niraparib are nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and hypertension.