Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide is a type of bioactive nucleotide used to treat black tongue and pellagra. Apart from that, this drug is also used in animals as a potential neuroprotective and anti-aging agent. Nicotinamide mononucleotide is also used to improve muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. Beta-Nicotinamide mononucleotide also reduces the adverse effects of glucose intolerance in type 2 diabetes.
Enquire Now
What is Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide?
Product Description
Molar Mass: 334.221
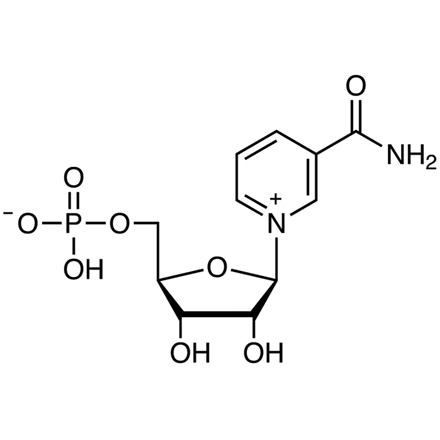
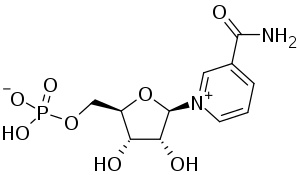
SMILES: c1cc(c[n+](c1)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)COP(=O)(O)[O-])O)O)C(=O)N
InChIKey: DAYLJWODMCOQEW-TURQNECASA-N
ALogP: 0.18
CAS Number: 1094-61-7
Chemical Formula: C11H15N2O8P
Form: Tablets
Solubility: PBS (pH 7.2): 10 mg/ml
Storage: -20°C
Suitable for: Adults
IUPAC Name: [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(3-Carbamoylpyridin-1-ium-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl hydrogen phosphate
Approved Indications: 3
As per the clinical trials, there is one approved indication of the Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide drug:
- Anemia
- Anemia, Iron-Deficiency
- Pellagra
Experimental Indications: 92
As per clinical trials 1-4, the drug can be used in the following categories:
- Acidosis, Lactic (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Acne Vulgaris (Phase 4)
- Acute Kidney Injury (Phase 3)
- Aging (Phase 2)
- Alcohol Withdrawal Delirium (Phase 3)
- Alzheimer’s Disease (Phase 2)
- Anemia, Sickle Cell (Phase 1)
- Antineoplastic Combined Chemotherapy Protocols (Phase 2)
- Arthritis, Rheumatoid (Phase 3)
- Ataxia Telangiectasia (Phase 2)
- Atherosclerosis ()
- Biological Availability (Phase 2)
- Blood Pressure (Phase 2)
- Breast Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Basal Cell (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Carcinoma, Squamous Cell (Phase 2)
- Cognition Disorders (Phase 3)
- Cognitive Dysfunction (Phase 3)
- Coronary Artery Disease (Phase 2)
- COVID-19 (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Deficiency Diseases (Phase 3)
- Depressive Disorder, Treatment-Resistant (Phase 2)
- Diabetes Mellitus (Phase 2)
- Diabetic Neuropathies (Phase 3)
- Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions (Phase 2)
- Eye Diseases ()
- Frailty (Phase 2)
- Friedreich Ataxia (Phase 2)
- Graft vs. Host Disease (Phase 3)
- Graves Ophthalmopathy (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Growth Disorders (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Head Injuries, Closed (Phase 3)
- Healthy Volunteers (Phase 4)
- Heart Failure (Phase 1)
- Heart Failure, Diastolic (Phase 2)
- Heart Failure, Systolic (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (Phase 1)
- Hodgkin Disease (Phase 1)
- Hyperphosphatemia (Phase 2)
- Hyperpigmentation (Phase 4)
- Hypertension (Phase 4)
- Hypertension, Pregnancy-Induced (Phase 1)
- Inflammation (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Intestinal Diseases (Phase 3)
- Jaundice, Obstructive (Phase 3)
- Keratosis, Actinic (Early Phase 1)
- Kidney Diseases (Phase 2)
- Kidney Failure, Chronic (Phase 3)
- Lactation Disorders (Phase 3)
- Leukemia, Lymphocytic, Chronic, B-Cell (Phase 2)
- Lupus Erythematosus, Cutaneous (Phase 2)
- Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma (Phase 1)
- Lymphoma, B-Cell (Phase 1)
- Lymphoma, Follicular (Phase 1)
- Lymphoma, Large B-Cell, Diffuse (Phase 1)
- Lymphoma, Mantle-Cell (Phase 1)
- Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin (Phase 1)
- Magnesium Deficiency (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Malnutrition (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Melanoma (Phase 2)
- Melanosis (Early Phase 1)
- Metabolic Diseases (Phase 1)
- Mitochondrial Diseases (Phase 1)
- Mortality (Phase 3)
- Multiple Myeloma (Phase 1)
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Phase 3)
- Myocardium (Phase 2)
- Neoplasm Metastasis (Phase 3)
- Neurodegenerative Diseases (Phase 2)
- Niacinamide (Phase 3)
- Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Phase 2)
- Obesity (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Ovarian Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Oxidative Stress (Phase 2)
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (Phase 3)
- Pharmacokinetics (Phase 1)
- Polycystic Kidney Diseases (Phase 2)
- Pre-Eclampsia (Phase 2)
- Premature Birth (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Psoriasis (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Recovery of Function (Phase 1)
- Renal Dialysis (Phase 3)
- Renal Insufficiency, Chronic (Phase 3)
- Reperfusion Injury (Phase 2)
- Retinitis Pigmentosa (Early Phase 1)
- Sarcopenia (Phase 2)
- Schizophrenia (Phase 4)
- Shock, Septic (Phase 3)
- Small Fiber Neuropathy (Phase 2)
- Urinary Bladder Neoplasms (Phase 3)
- Vascular Diseases (Phase 2)
- Wernicke Encephalopathy (Phase 2/Phase 3)
Clinical Trials:
128 trials took place for Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in four phases. 185 organizations participated in these trials.
Side Effects:
Major side effects observed after the consumption of Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide are:
- Nausea
- Stomach Discomfort
- Headache
Product CAS No
1094-61-7
Therapeutic Action
Beta-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (“NMN” and “β-NMN”) is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide. … Because NADH is a cofactor for processes inside mitochondria, for sirtuins, and for PARP, NMN has been studied in animal models as a potential neuroprotective and anti-aging agent.
Conclusion
Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide is a type of bioactive nucleotide that reduces glucose levels in type-2 diabetes. It is also a nice anti-aging agent in animals. Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide has a molar mass of 334.221 g/mol and is suitable for adults. There are many other experimental indications of Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, including psoriasis, urinary bladder neoplasm, renal dialysis, etc.