Veliparib is a PARP (poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase) inhibitor used to treat cancer. It treats metastatic melanoma, NSCLC, prostate cancer, and brain tumors associated with primary metastatic tumors. Veliparib blocks a protein called PARP, thereby preventing the repair of the cancer cells and making them prone to anti-cancer drugs. Besides the above cancer type, Veliparib is still under evaluation for treating ovarian cancer.
Enquire Now
What is Veliparib?
Product Description
Molar Mass: 244.298
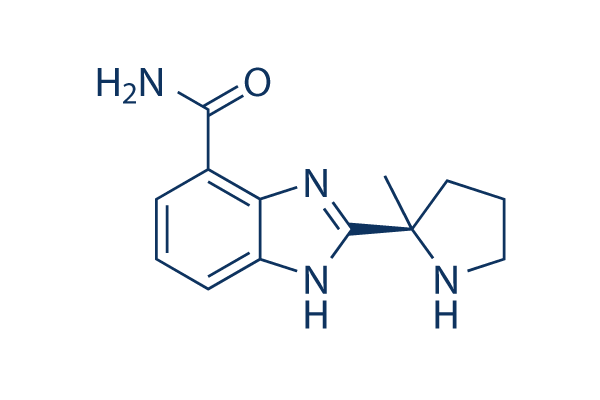
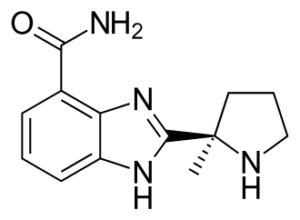
SMILES: C[C@]3(c2nc1c(C(N)=O)cccc1[nH]2)CCCN3
InChIKey: NAHVYVRKWKWKQ-CYBMUJFWSA-N
ALogP: 1.26
CAS Number: 912444-00-9
Chemical Formula: C13H16N4O
Form: Tablets
Solubility: DMF: 0.25 mg/ml, DMSO: 15 mg/ml, Ethanol: 0.1 mg/ml, PBS (pH 7.2): 10 mg/ml
Storage: -20°C
Suitable for: Adults
IUPAC Name: 2-((R)-2-Methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide
Approved Indications: 0
Experimental Indications: 108
As per clinical trials 1-4, the drug can be used in the following categories:
- Adenocarcinoma of the Lung (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Adrenal Gland Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Astrocytoma (Phase 2)
- Bile Duct Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Brain Diseases (Phase 1)
- Brain Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- BRCA1 Protein (Phase 2)
- Breast Neoplasms (Phase 3)
- Breast Neoplasms, Male (Phase 1)
- Brenner Tumor (Phase 1)
- Burkitt Lymphoma (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma (Phase 1)
- Carcinoma, Hepatocellular (Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Merkel Cell (Phase 1)
- Carcinoma, Neuroendocrine (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung (Phase 3)
- Carcinoma, Renal Cell (Phase 1)
- Carcinoma, Small Cell (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Carcinoma, Transitional Cell (Phase 1)
- Central Nervous System Diseases (Phase 1)
- Choroid Plexus Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Colonic Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Colorectal Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Craniopharyngioma (Phase 1)
- Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma (Phase 1)
- DNA Mismatch Repair (Phase 1)
- Endometrial Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Ependymoma (Phase 1)
- Esophageal Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Fallopian Tube Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Gallbladder Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Glioblastoma (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Glioma (Phase 2)
- Gliosarcoma (Phase 2/Phase 3)
- Hamartoma (Phase 2)
- Hemangiosarcoma (Phase 2)
- Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome (Phase 1)
- Hodgkin Disease (Phase 2)
- Intestinal Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Intraocular Lymphoma (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Leukemia (Phase 1)
- Leukemia, Hairy Cell (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Lymphocytic, Chronic, B-Cell (Phase 2)
- Leukemia-Lymphoma, Adult T-Cell (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Monocytic, Acute (Phase 1)
- Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Myeloid, Chronic, Atypical, BCR-ABL Negative (Phase 2)
- Leukemia, Myelomonocytic, Acute (Phase 1)
- Leukemia, Myelomonocytic, Chronic (Phase 2)
- Liver Failure (Phase 1)
- Liver Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Lung Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, B-Cell, Marginal Zone (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, Follicular (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, Large-Cell, Anaplastic (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, Large-Cell, Immunoblastic (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, Mantle-Cell (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin (Phase 2)
- Lymphoma, T-Cell (Phase 2)
- Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis (Phase 2)
- Medulloblastoma (Phase 1)
- Melanoma (Phase 2)
- Meningioma (Phase 1)
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (Phase 1)
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2a (Phase 1)
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2b (Phase 1)
- Multiple Myeloma (Phase 2)
- Mutation (Phase 2)
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes (Phase 1)
- Myeloproliferative Disorders (Phase 2)
- Neoplasm Metastasis (Phase 1)
- Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Neoplasms, Germ Cell, and Embryonal (Phase 1)
- Nervous System Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Neuroectodermal Tumors (Phase 1)
- Neuroectodermal Tumors, Primitive (Phase 1)
- Neuroendocrine Tumors (Phase 1)
- Oligodendroglioma (Phase 1)
- Oropharyngeal Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Ovarian Diseases (Phase 1)
- Ovarian Neoplasms (Phase 3)
- Pancreatic Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Peritoneal Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Pheochromocytoma (Phase 1)
- Polycythemia Vera (Phase 2)
- Precursor B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma (Phase 2)
- Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma (Phase 1)
- Primary Myelofibrosis (Phase 2)
- Prostatic Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Prostatic Neoplasms, Castration-Resistant (Phase 2)
- Renal Insufficiency (Phase 1)
- Rhabdoid Tumor (Phase 1)
- Sezary Syndrome (Phase 2)
- Skin Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (Phase 2)
- Spinal Cord Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Stomach Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Testicular Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Thrombocythemia, Essential (Phase 2)
- Thymoma (Phase 1)
- Thyroid Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Triple-Negative Breast Neoplasms (Phase 3)
- Urinary Bladder Neoplasms (Phase 1)
- Uterine Cervical Neoplasms (Phase 2)
- Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia (Phase 1/Phase 2)
- Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (Phase 1)
Clinical Trials:
FDA held a total of 102 trials for Veliparib in four phases. Fifty (50) organizations took part in these trials.
Side Effects:
Major side effects observed after the consumption of Veliparib are:
- Anemia
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Vomiting
Product CAS No
912444-00-9
Therapeutic Action
Veliparib (ABT-888) is a PARP inhibitor being investigated to treat non-small cell lung cancer, BRCA breast cancer, and ovarian cancer.
Conclusion
Veliparib is an anti-cancer drug that falls under the class of medications called poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors. It kills cancer cells by eliminating the restructuring of their DNA and making them prone to anti-cancer drugs. Veliparib has a molar mass of 244.29 g/mol and is stored at room temperature. Some common side effects of this drug are vomiting, nausea, and fatigue.