Table of Contents
What is Sacubitril
Sacubitril is a drug used to treat heart failure with a low ejection fraction. It functions by preventing the Neprilysin enzyme from functioning. It aids in raising the concentrations of peptides, which encourages vasodilation and lessen sodium retention in the kidneys. It also improves the cardiac function.
Valsartan, an angiotensin receptor blocker that aids in blood vessel relaxation and blood pressure lowering, it is used along with sacubitril API. These two medications are collectively known as LCZ696.
Sacubitril is known as a standard medication in several nations after clinical trials showed that it reduce the likelihood of heart failure hospitalizations and improved symptoms. It is important to remember Sacubitril is not suitable for everyone.
Use of Sacubitril
It is the medication used to treat heart failure along with reduced ejection fraction. This works by inhibiting the activity called neprilysin, which involves the breakdown of several hormones and peptides which is involved in the breakdown of the several hormones and peptides which can affect blood pressure and fluid balance.
With the combination of angiotensin receptor blockers valsartan, it is used for reducing the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization with HFrEF.
Pharmaceutical raw materials used in the making of Sacubitril have been shown to be more effective than the standard treatment of ACE inhibitors in reducing the risk of death and hospitalization. However, it is important to note this kind of medication is not appropriate for all patients who have been diagnosed with heart disease. They should not use it without the guidance of the healthcare provider.
Side Effects of Sacubitril
Sacubitril is used for treating heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Like all other medications, it also has side effects. Here are some of the most common side effects of Sacubitril, that includes:
- Dizziness
- Hypotension
- Hyperkalemia
- Cough
- Diarrhoea
- Elevated serum creatinine
Some of the rare side effects of Sacubitril include:
- Angioedema (swelling of the lips, face, tongue, or throat)
- Rash
- Liver function abnormalities
- Neutropenia (low levels of white blood cells)
- Increased uric acid levels
- Hypersensitivity reactions
It is high time that you should talk to your healthcare provider if you experience any of these side effects while taking Sacubitril.
Precautions of Sacubitril
Sacubitril is the medication used to treat heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction. It is crucial to take the following precautions while using Sacubitril:
- Inform the healthcare expert about the medical conditions you have or any medication you are taking before using Sacubitril.
- Do not take Sacubitril in case you are allergic to it or any of its specific ingredients.
- Use Sacubitril with caution in case you have a history of angioedema.
- It may cause hypertension, especially during the first week of the treatment. The healthcare expert may need to adjust your dose and monitor your blood pressure accordingly.
- It increases the risk of hyperkalemia. The healthcare provider may need to monitor the potassium level when you start taking Sacubitril.
- It may interact with other medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics, and potassium supplements. Inform the healthcare provider about the other medications you are taking before using Sacubitril.
- During pregnancy or breastfeeding, Sacubitril is not recommended. Consult the healthcare provider before taking medicine.
Always follow the advice of the healthcare provider’s instructions while using Sacubitril and inform them immediately if you experience any kind of side effects or have any concerns.
Chemical composition
Sacubitril is the neprilysin inhibitor prodrug with natriuretic activity. It comes with the combination of valsartan in order to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in any patient. The active metabolite present in Sacubitril, LBQ657 inhibits neprilysin, which is a neutral endopeptidase and cleaves natriuretic peptides such as atrial natriuretic endopeptidase. API manufacturers are trying their best to develop the efficacy of these drugs.
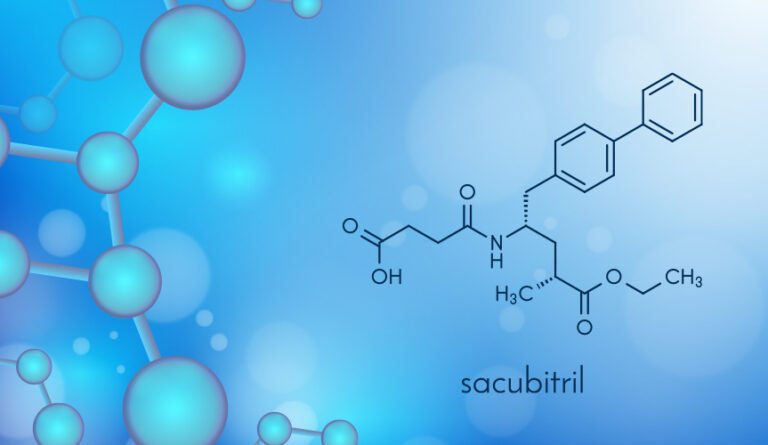
The molecular formula of Sacubitril is C24H29NO5.
The molecular weight of Sacubitril is 411.5 g/mol.
The IUPAC name of Sacubitril is 4-{[(2S,4R)-1-(4-Biphenylyl)-5-ethoxy-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-pentanyl]amino}-4-oxobutanoic acid
Conclusion
Sacubitril is the neprilysin inhibitor used in combination with Valsartan as the adjunct to reduce the potential risk of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure in patients. It is an effective medication for chronic heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. If you have any queries regarding the ingredients, pharmaceutical raw materials, and chemical compositions, you can always reach out to Bulat Pharmaceutical. Our crew members are here to resolve all your queries.